RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS (MISSCARRIAGE)
What is Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (Miscarriage)?
A miscarriage is the spontaneous termination of a pregnancy before 24 weeks. If this occurs two or more times, it is called recurrent miscarriage. This includes miscarriages that occur naturally or after IVF treatment, but does not include ectopic pregnancies or molar pregnancies (grape pregnancies).
This condition is important to recognize because it requires a thorough physical examination and a series of tests to investigate the cause.
About 15% of pregnancies end in miscarriage. Recurrent pregnancy loss occurs in 1 to 2% of couples.
What are the Causes of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (Miscarriage)?
- Genetic problems in the fetus: The fetus (the medical term for a baby in the womb from the 9th week of pregnancy until delivery) may have genetic problems caused by the fusion of the egg and sperm cells. This can happen by chance, or sometimes due to certain diseases in the parents’ genetics or advanced maternal age.
- Uterine abnormalities: The uterus may have malformations.
- Autoimmune diseases: The mother’s immune system (autoimmune) cells attack healthy tissue.
- Other medical conditions in the mother: These can include diabetes, thyroid disease, blood clotting problems, or hormonal problems.
- Unexplained causes: In 50-75% of women with recurrent miscarriages, no cause for the pregnancy loss can be found. There may be clues as to what the problem is, but there is no definitive answer.
What is the Most Common Known Cause of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (Miscarriage)?
The most common cause is an abnormal number of chromosomes in the fetus. This accounts for about 60% of miscarriages with genetic abnormalities. This usually happens by chance, but the risk increases with advanced maternal age.
Can Other Genetic Problems Cause Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
Chromosomes are tightly coiled packages of DNA found in the nucleus of almost all cells in living organisms. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Sometimes, at least one of the partners has a condition called a balanced translocation. This means that part of a chromosome from one of the partners has moved to another chromosome. When there is a balanced translocation, there are no physical signs or symptoms, but the egg or sperm can produce an abnormal chromosome, resulting in an unhealthy fetus that miscarries.
Can Uterine Abnormalities Cause Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
Some congenital uterine malformations can cause recurrent miscarriages. The most common uterine malformation associated with this is uterine septum, also known as a uterine septum. This is a partial wall in the uterus that divides the uterine cavity into two separate compartments.
Myomas and polyps in the uterine lining and wall can also play a role in recurrent pregnancy loss.
Can Blood Clotting Problems Cause Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a condition in which a person’s immune system develops antibodies against certain substances involved in their own blood clotting.
What Diseases Can Cause Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
Another disease that can lead to miscarriage is diabetes mellitus. In this disease, blood sugar levels are higher than normal. Women with diabetes, especially those with poorly controlled and high blood sugar levels, are at increased risk of miscarriage. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome are also at increased risk of miscarriage.
What Tests Should Be Done on Patients with Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
The evaluation should begin by taking a detailed medical history, including menstrual cycle and past pregnancies.
A detailed ultrasound examination of the uterus and reproductive organs should be performed.
Blood tests should be performed. These tests include tests that measure the immune system, blood clotting system, and hormone levels. Tests may also be done to check for other medical conditions such as thyroid disease or diabetes.
If necessary, an imaging test called HSG may be done to check the uterus. Your doctor may order this test, called a hysterosalpingogram, to check the lining of the uterus. If necessary, your doctor may also perform a hysteroscopy, a procedure that uses a camera inserted through the vagina to look inside the uterus.
Genetic testing may be done on you and your partner, and even on previous miscarriage material if necessary.
Remember! The tests to be requested are related to the person’s medical condition and are specific to the individual.
Is Treatment for Recurrent Pregnancy Loss Possible?
If the cause of recurrent pregnancy loss is found, there are treatment options to address the cause.
What Can Be Done if I Have a Chromosome Translocation?
If you have a chromosome translocation, genetic counseling may be recommended. In these cases, a special genetic test called “preimplantation genetic diagnosis” (PGD) can be performed. This means that your pregnancy is planned through IVF and the embryos are genetically tested before being transferred to your uterus. Genetically healthy embryos are transferred to your uterus and a healthy pregnancy is expected.
How Are Uterine Abnormality Problems Treated?
Depending on the type of uterine abnormality, surgery can be used to correct it in some cases. Uterine septum is one of the uterine malformations that we frequently encounter and achieve successful treatment results.
The patient you see below is a 25-year-old woman who presented with a desire to become pregnant. The images below show her pre- and post-operative hysterosalpingograms. The uterine septum was completely removed in surgery.
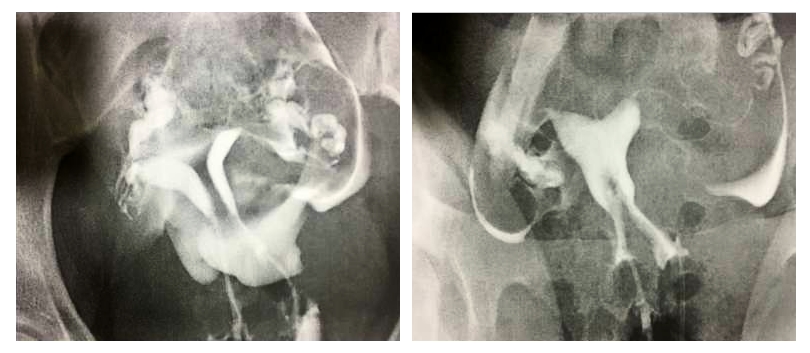
Another patient of mine is a 31-year-old woman who has had 2 miscarriages. She has a uterine septum and a vaginal septum. The pre- and post-operative images are as follows.
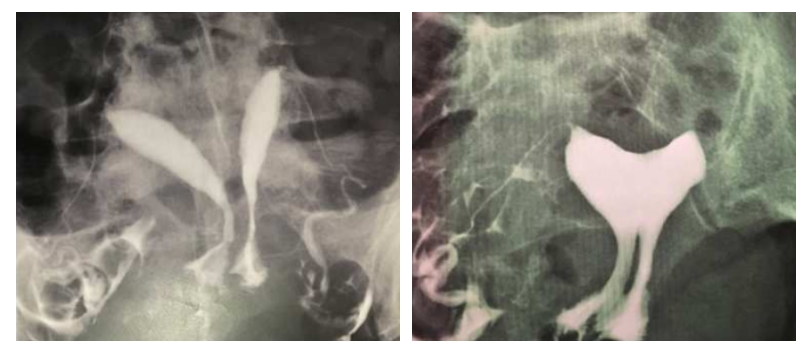
What Treatment Can Be Used i f I Have Antiphospholipid Syndrome?
Low-dose aspirin may be prescribed along with blood thinners such as heparin throughout pregnancy. This treatment can increase the successful pregnancy rates in women with this condition.
What Are My Chances of a Successful Pregnancy If No Cause Is Found After All Tests?
If no cause can be found in women with unexplained miscarriages, the chance of a successful pregnancy in their next pregnancy is 65%.



